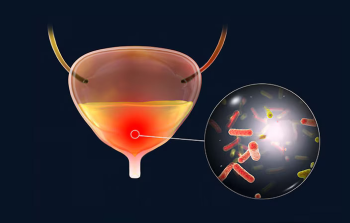
Recurrent urine infections, also known as recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs), occur when a person experiences multiple episodes of infection in the urinary tract. This can affect any part of the urinary system, including the bladder, urethra, ureters, or kidneys. Some bacteria may be resistant to antibiotics, making infections harder to treat. Structural abnormalities in the urinary tract can predispose individuals to frequent infections. Factors such as improper hygiene, frequent sexual activity, or using certain contraceptives can contribute to recurrent UTIs.